Transforms
Meshes can be transformed in 3D space using the position, rotation and scale properties. These properties are vectors, which means they are arrays of numbers.
Let's start by a bit of theory.
Axes
In a 3D space, there are three axes: x, y, and z. Each axis is a line that extends infinitely in both directions.
The axes are perpendicular to each other, which means they form a right angle at their intersection.
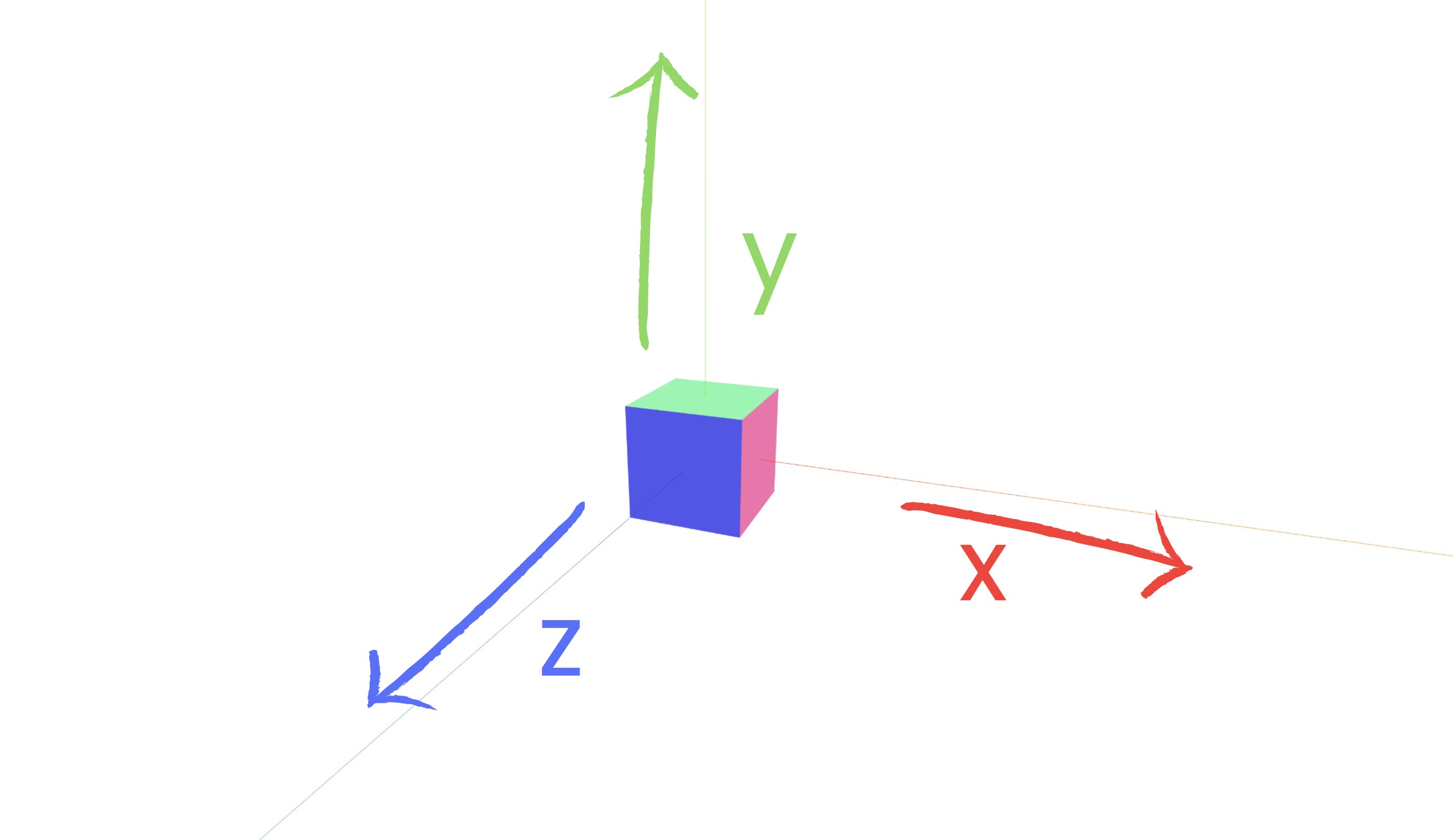
With Three.js the axes are defined as follows:
x: points to the righty: points upz: points towards the viewer
Vector3
Vectors are used to represent points in 3D space. They are made of three numbers, one for each axis (x, y, z).
With Three.js you can create vectors using the Vector3 class. This class is part of the three package, so you can import it like this:
import { Vector3 } from "three";
You can create a vector by passing the x, y, and z coordinates to the Vector3 constructor:
const vector = new Vector3(1, 2, 3);
Threejs Vector 3 documentation
Position
The position property is a 3D vector but thanks to r3f you can pass it as an array of numbers. Under the hood, r3f will convert the array to a Vector3 object and react to changes. Most properties in r3f work this way.
The default value for the position property is [0, 0, 0]:
<mesh position={[0, 0, 0]} />
Download the starter pack and run yarn to install the dependencies and yarn dev to start the development server.
You should see a green cube in the middle of the screen:
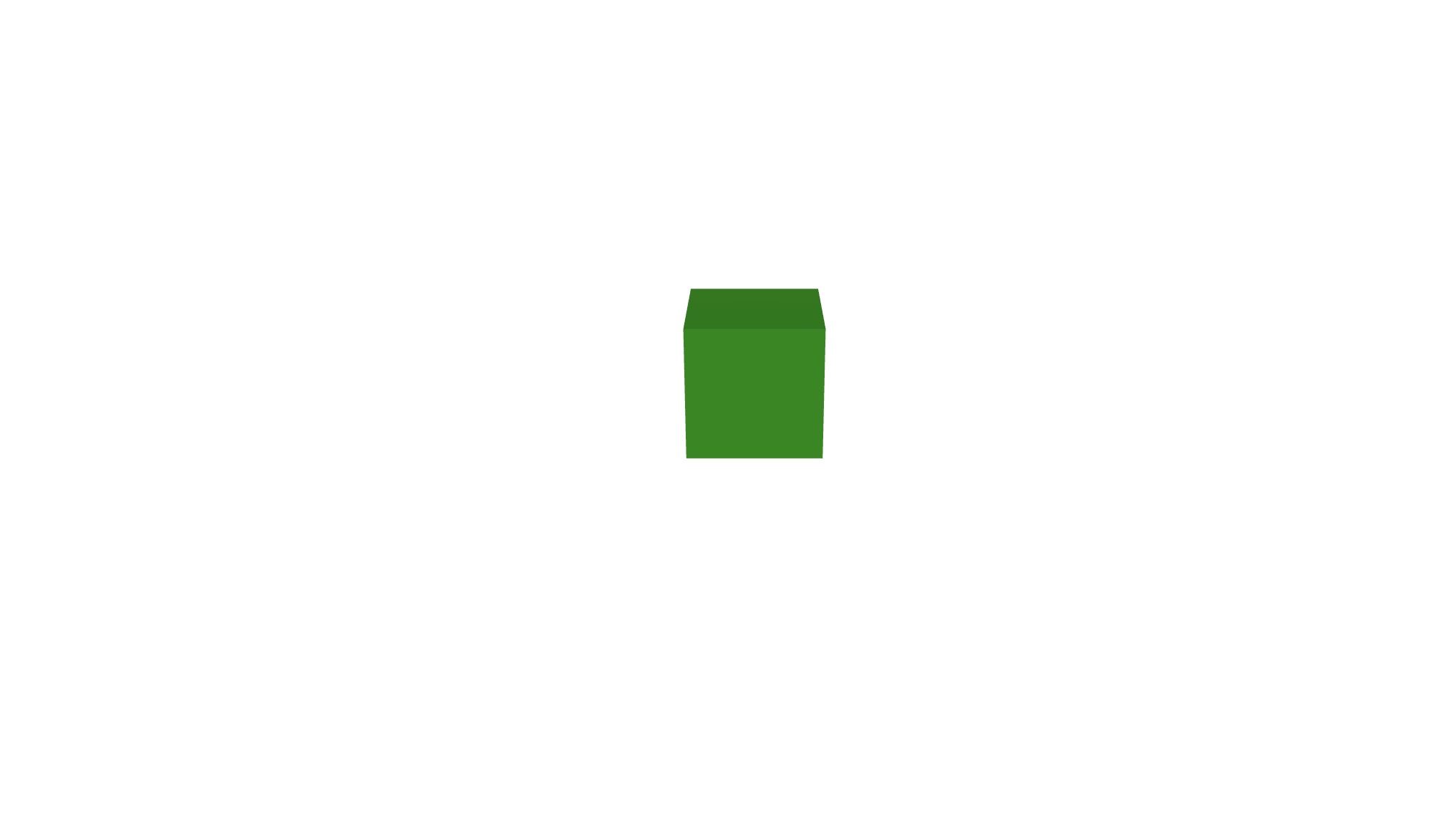
In fact there are 3 cubes at the exact same position.
Let's play with the x, y, and z coordinates to move the cubes around.
Let's try to align them on the different axes.
React Three Fiber: The Ultimate Guide to 3D Web Development
✨ You have reached the end of the preview ✨
Go to the next level with Three.js and React Three Fiber!
Get full access to this lesson and the complete course when you enroll:
- 🔓 Full lesson videos with no limits
- 💻 Access to the final source code
- 🎓 Course progress tracking & completion
- 💬 Invite to our private Discord community
One-time payment. Lifetime updates included.